Across diverse sectors—from consumer electronics to automotive, medical devices to personal protection—precision injection molds enable high-volume, high-quality production of plastic parts. In this article, we explore the common injection molds used in different industries, their key characteristics, and how an experienced injection mold manufacturer like RUNKE can support clients from concept through mass production.
Understanding Injection Molds and Their Role
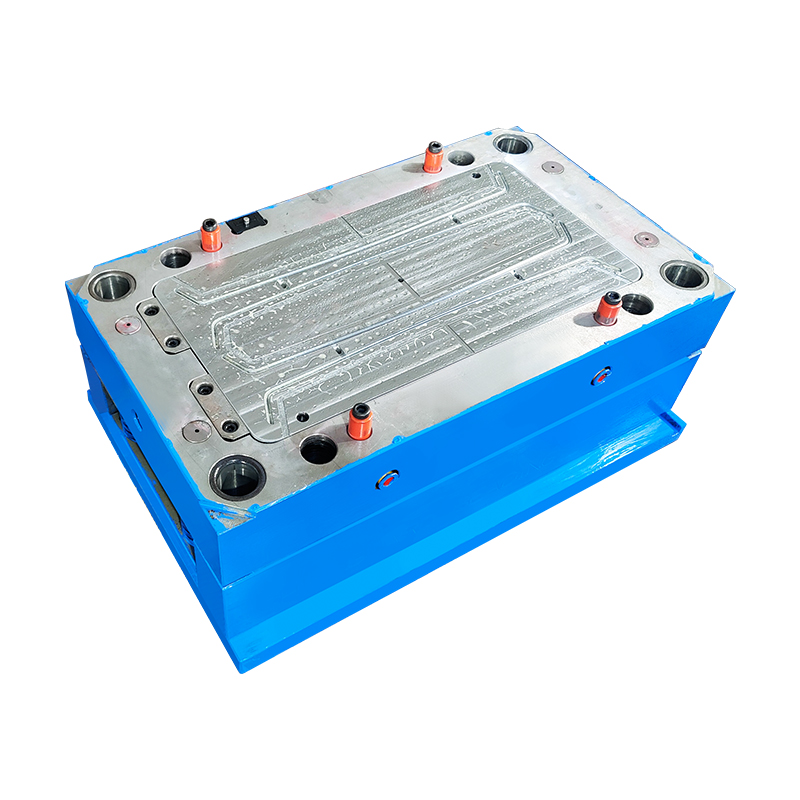
An injection mold is a precision tool, usually made of hardened steel or aluminum, into which molten polymer is injected under high pressure, cooled, and ejected as a finished plastic part.
A well-engineered mold determines part quality, dimensional accuracy, and production efficiency. Good mold design ensures minimal cycle time, consistent performance, and long service life.
Modern design techniques—such as reverse engineering, DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis, and mold flow analysis—help identify and prevent potential defects like warpage, sink marks, weld lines, and uneven cooling before the mold is built.
With full 2D & 3D mold design capability, RUNKE ensures every mold aligns perfectly with the client's product design, CAD data, or technical drawings—offering shorter lead times, higher accuracy, and integrated engineering support.
Common Injection Molds in Different Industries
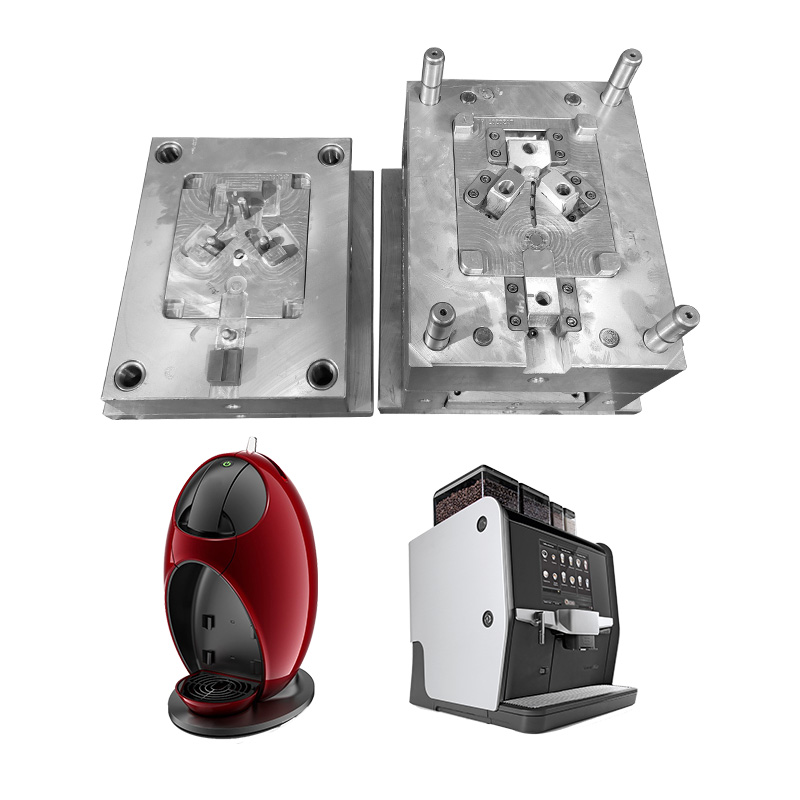
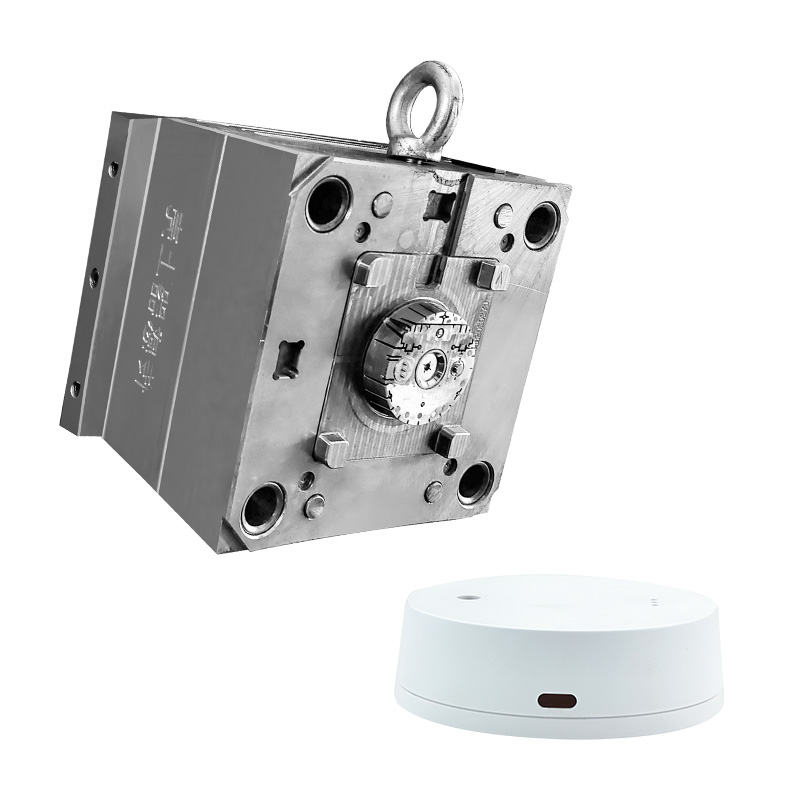
1. Precision Electronics & Consumer Appliances
The electronics and appliance sectors require compact, durable components with complex geometries and aesthetic surfaces. Molds must deliver tight tolerances and support multi-material overmolding.
Specific mold:
● Smartphone shell mold: For outer housings and back covers with ultra-thin walls and smooth surfaces.
● Connector housing mold: For precise electrical connector parts requiring micron-level accuracy.
● Switch button mold: Used in home appliances, designed for frequent mechanical operation.
● Camera lens holder mold: Requires high dimensional stability and precise alignment features.
● Electronic enclosure mold: For IoT devices or chargers, typically designed with snap-fit features.
Common mold types:
● Micro-precision injection molds
● Insert overmolding molds
● Two-shot or multi-shot molds
● Hot runner molds
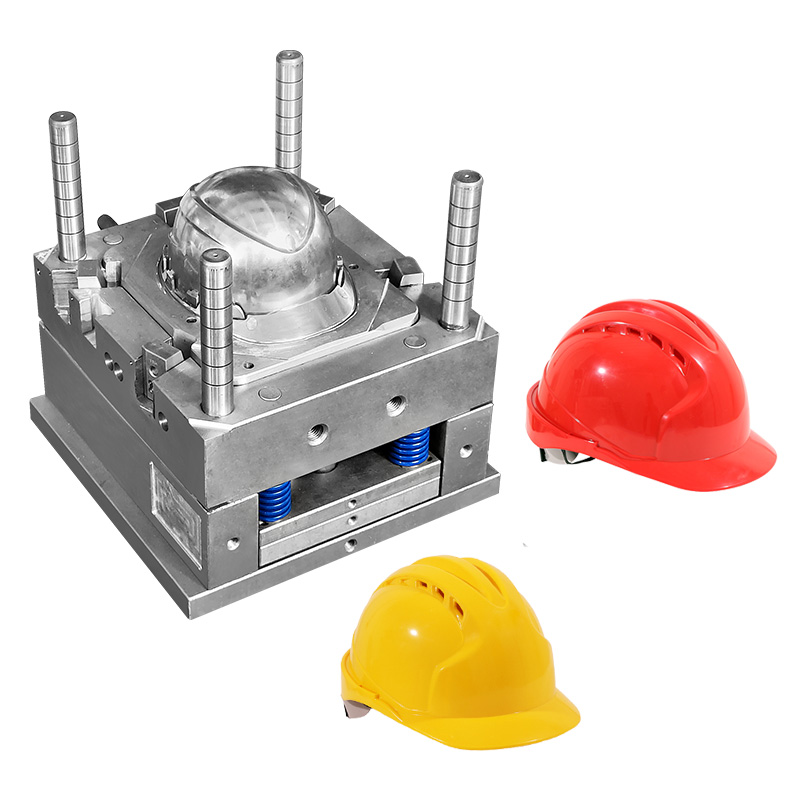
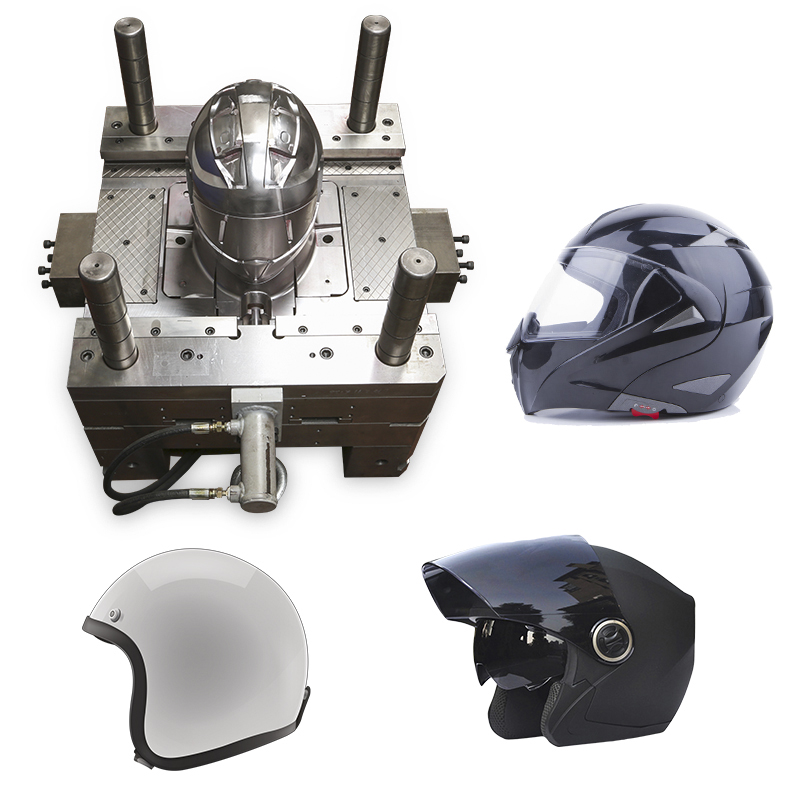
2. Personal Safety Product Molds (Goggles, Helmets, Gas Masks, Face Shields)
The personal protection industry requires components that meet high standards for strength, transparency, comfort, and safety. These molds demand a superior surface finish and a precise fit.
Specific mold:
● Gas mask injection mold: Used for producing the facepiece and filter housing of respirators. Requires precision sealing surfaces and flexible material overmolding.
● Safety goggle frame mold: For optical-grade frames that hold lenses securely and maintain comfort during long use.
● Helmet visor mold: Produces impact-resistant, transparent visors with excellent optical clarity.
● Face shield bracket mold: For strong, lightweight supports used in protective face shields.
Common mold types:
● Optical-grade injection molds
● Gas-assisted or core-back molds
● Two-component (co-injection) molds
● Thick-to-thin section molds
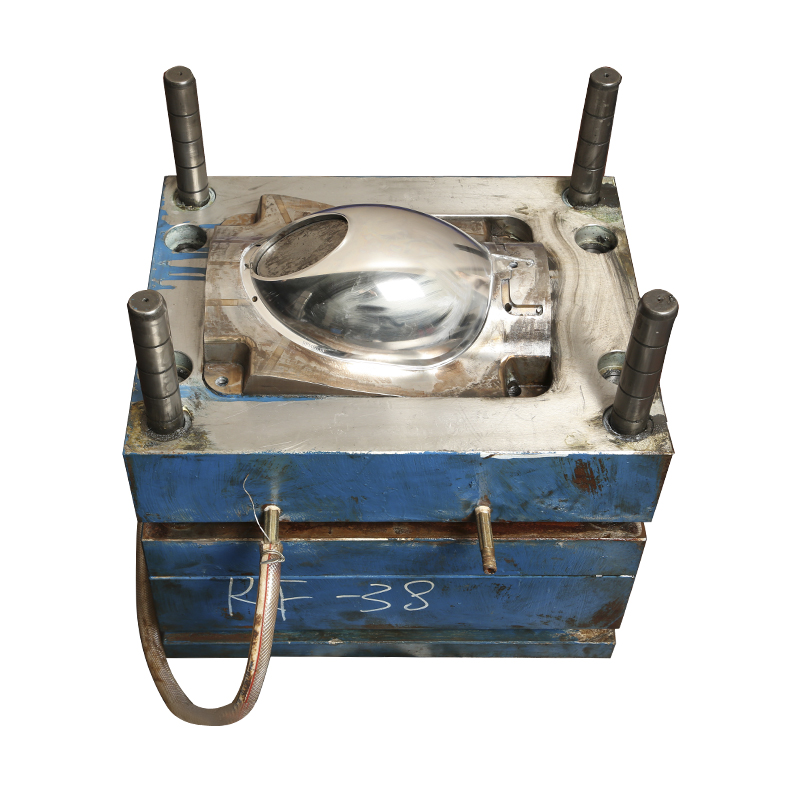
3. Automotive & Auto Accessory Molds
The automotive sector relies heavily on plastic components for weight reduction, design flexibility, and cost efficiency. Parts include everything from decorative trims to structural housings.
Specific mold:
● Car bumper mold: A large-format injection mold requiring excellent cooling balance and surface texture.
● Dashboard panel mold: Designed for dimensional accuracy and consistent texture finish.
● Headlamp housing mold: Demands high optical precision and heat resistance.
● Door handle mold: Involves insert molding for metal reinforcements and decorative finishes.
● Grille and trim mold: For exterior aesthetics and aerodynamic performance.
Common mold types:
● Large-scale injection molds with robust cooling
● Multi-cavity or family molds
● Molds with side-actions or gas-assist systems
● Insert and overmolding molds
4. Medical & Healthcare Product Molds
Medical devices require absolute precision, biocompatibility, and cleanliness. Molds used for medical applications must meet strict industry standards and support sterile manufacturing environments.
Specific mold:
● Medical syringe mold: Multi-cavity high-speed mold used for disposable syringes and plungers.
● IV connector mold: Small, tight-tolerance molds ensuring leak-free assembly.
● Test tube cap mold: Used in laboratories, requiring smooth surfaces and dimensional stability.
● Inhaler housing mold: For portable drug delivery devices, combining rigid and flexible plastics.
● Medical valve mold: For flow control systems in IV sets or diagnostic equipment.
Common mold types:
● Cleanroom-grade precision molds
● Micro-molding molds
● Thin-wall molds
● Insert and overmolding molds
Medical Safety Goggle Frame Mold
5. Construction & Industrial Molds
In construction and heavy industries, injection molding is used for functional, durable components such as brackets, joints, and protective housings. These molds must endure high wear and produce cost-effective parts.
Specific mold:
● Pipe fitting mold: For water or gas connection systems requiring leak-proof threads and tight tolerances.
● Electrical conduit box mold: Produces durable enclosures for industrial wiring systems.
● Tool handle mold: For power tools and industrial equipment with ergonomic grips.
● Clamp and bracket mold: Used in structural fixtures and supports.
● Construction anchor plug mold: For wall anchors or expansion plugs used in installations.
Common mold types:
● Single-cavity and multi-cavity molds
● Hot-runner molds
● Stack molds
● Gas-assisted molds
Construction Industry Mold - Building Plastic Mold
6. Motorcycle & Specialty Accessory Molds
Motorcycle accessories require high durability, weather resistance, and visual appeal. Molds must support complex geometries and precise alignment between interconnected components.
Specific mold:
● Motorcycle fairing mold: Large molds producing aerodynamic panels with uniform wall thickness.
● Helmet shell mold: For outer protective shells with high impact strength.
● Tail light lens mold: Optical-grade transparent molds for lighting components.
● Handlebar grip mold: Overmolding mold combining soft TPE and rigid ABS.
● Side cover mold: Structural cover mold ensuring perfect fit and finish.
Common mold types:
● Large-format molds
● Insert and hybrid molds
● Gas-assisted molds
● Side-action molds
Motorcycle Helmet Shell Plastic Mold
Summary Table of Common Injection Molds by Industry
| Industry / Application | Typical Mold Examples | Key Design Considerations |
| Precision Electronics / Appliances | Smartphone shell mold, connector housing mold, camera lens holder mold | Tight tolerances, uniform cooling, small gates |
| Personal Safety (Visors, Goggles, Helmets) | Gas mask mold, goggle frame mold, helmet visor mold | Surface finish, stress/warpage control |
| Automotive & Auto Accessories | Bumper mold, dashboard mold, headlamp housing mold, door handle mold | Structural rigidity, consistent fill, lifecycle |
| Medical & Healthcare | Syringe mold, IV connector mold, inhaler housing mold, valve mold | Tolerances, cleanliness, biocompatibility |
| Construction & Industrial | Pipe fitting mold, conduit box mold, clamp mold, tool handle mold | Cost optimization, robustness, productivity |
| Motorcycle Accessories | Fairing mold, helmet shell mold, tail light lens mold | Vibration durability, wall uniformity, surface aesthetics |
RUNKE: Your Comprehensive Mold Solution Partner
RUNKE offers end-to-end mold design and manufacturing solutions, capable of transforming customer designs or specifications into production-ready molds.
✅ Reverse Engineering – Scanning and reproducing parts for redesign or improvement.
✅ DFM Analysis – Early feedback to ensure product geometry is suitable for molding.
✅ Mold Flow Analysis – Predicting potential defects like warpage or weld lines before manufacturing.
✅ Full 2D & 3D Mold Design – Comprehensive digital design ensuring precise tooling.
✅ Tool Fabrication and Testing – CNC machining, EDM, assembly, and validation.
✅ Maintenance and Optimization – Post-delivery support, repairs, and performance improvement.
From precision electronic molds to auto accessory molds and medical product molds, RUNKE ensures high-performance tooling across multiple industries—delivering efficiency, durability, and exceptional part quality.
Best Practices for Customers Developing Injection Mold Projects
● Provide detailed 2D/3D product drawings and define tolerances early.
● Conduct DFM analysis during the design phase to reduce costly revisions.
● Use mold flow analysis to ensure balanced filling and avoid defects.
● Maintain consistent wall thickness to prevent sink marks and stress.
● Optimize gate and runner layout for multi-cavity molds.
● Plan cooling systems to achieve uniform temperature control.
● Consider maintenance schedules to extend mold lifespan.
Conclusion
Injection molding continues to be one of the most versatile and efficient manufacturing methods across industries—from precision electronics and medical devices to automotive, construction, and personal safety equipment. Each industry demands specific mold types, materials, and technical standards, and choosing the right injection mold manufacturer is key to achieving consistent, high-quality production results.
With years of expertise and advanced design capabilities, RUNKE provides end-to-end injection mold solutions, including reverse engineering, DFM analysis, mold flow analysis, and full 2D & 3D mold design.
Whether you need a custom mold design based on 3D models or optimization of an existing product for better manufacturability, RUNKE is a trusted partner that helps you turn ideas into reality.






.jpg)

.jpg)